Topological Sort
activity on vertex network
the definition in logic
摘抄自某EDU:
definition A directed graph in which the vertices represent tasks or activities and the edges represent precedence relations between tasks.
To be careful: 在AOV中是不能有cycles, 让一个activity的开始要以自身的结束为条件, 这显然是不合理的, 即: Directed Acyclic Graph
the definition in mathematics
这个definition本质上就是DAG的definition
definition A graph G = (V,E), V and E are two sets, each edge is represented by a ordered pairs <u,v> V: finite non-empty set of vertices E: set of pairs of vertices, edges
Example: a graph G
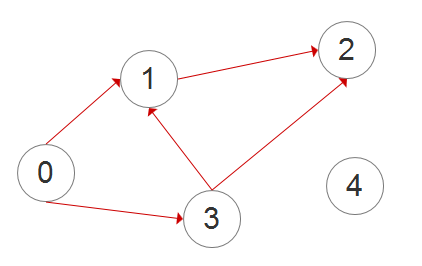
the realization in computer science
public class AOVNetwork {
private int V;//no and tag of vertices
private LinkedList<Integer> adjacency[];//adjacency list
public AOVNetwork(int v) {
V = v;
adjacency = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
adjacency[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
/**
* add an edge from v to w
* @param v
* @param w
*/
public void addEdge(int v, int w){
adjacency[v].add(w);
}
/**
* add edge from v to w1, w2, w3, ....
* @param v
* @param w
*/
public void addEdges(int v, int... w){
for (int ww : w) {
adjacency[v].add(ww);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AOVNetwork{" +
"V=" + V +
", adjacency=" + Arrays.toString(adjacency) +
'}';
}
}
topological sort
definition
摘抄自Wikipedia:
In the field of computer science, a topological sort or topological ordering of a directed graph is a linear ordering of its vertices such that for every directed edge uv from vertex u to vertex v, u comes before v in the ordering. For instance, the vertices of the graph may represent tasks to be performed, and the edges may represent constraints that one task must be performed before another
about partial order and total order
这是一个mathematic上的概念, partial order指的是: 在部分元素间的先后关系不确定的情况下而产生的排序, 如:
condition: x<=z, y<=z
result: x,y,z or y,x,z
而total order则是partial order的一个特例, 即: 在所有元素的先后关系都是完全确定的情况下而产生的排序, 如:
condition: x<=y, y<=z
result: x,y,z
如果topological sort是unique, 则说明该order是一个total order, 同时DAG存在hamiltonian path, 否则说明order是一个partial order
typical algorithms
解决topological sort的typical algorithms有两个:
- Kahn’s algorithm
- DFS
这两个algorithms的time complexity都是O(|V| + |E|), 由于DFS是一个十分强大和通用的algorithm, 为减小篇幅, 这里仅对Kahn’s algorithm进行介绍
Kahn’s algorithm
Kahn’s algorithm的伪代码:
L ← Empty list that will contain the sorted elements
S ← Set of all nodes with no incoming edge
while S is non-empty do
remove a node n from S
add n to tail of L
for each node m with an edge e from n to m do
remove edge e from the graph
if m has no other incoming edges then
insert m into S
if graph has edges then
return error (graph has at least one cycle)
else
return L (a topologically sorted order)
the realization in java
public List<Integer> topologicalSorting(){
LinkedList<Integer> sortedNodes = new LinkedList<>();//L, nodes that have bean sorted
Set<Integer> zeroIndegreeNodes = new TreeSet<>();//S, nodes with no incoming edge
LinkedList<Integer> transposeOfAdjacency[] = new LinkedList[V];//transpose of adjacency list
//transpose of adjacency init
IntStream.range(0, transposeOfAdjacency.length)
.forEach(n -> {
transposeOfAdjacency[n] = new LinkedList<>();
});
//tranform adjacency to transpose of adjacency
IntStream.range(0, transposeOfAdjacency.length)
.forEach(n -> {
adjacency[n].stream().forEach(m ->{
transposeOfAdjacency[m].add(n);
});
});
//zeroIndegreeNodes init
IntStream.range(0, transposeOfAdjacency.length)
.filter(i -> transposeOfAdjacency[i].size() == 0)
.forEach(i -> {
zeroIndegreeNodes.add(i);
});
//judge cycles
if (zeroIndegreeNodes.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("AOVNetwork has cycles");
return null;
}
//Kahn's algorithm begin
Iterator<Integer> iterator = zeroIndegreeNodes.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Integer n = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();//remove a node n from S
sortedNodes.addLast(n);//add n to tail of L
Iterator<Integer> mIterator = adjacency[n].iterator();
while (mIterator.hasNext()){
Integer m = mIterator.next();
mIterator.remove();//remove edge e from the graph
transposeOfAdjacency[m].remove(n);//remove edge e from the graph
//judge does m has no other incoming edges
if (transposeOfAdjacency[m].size() == 0){
zeroIndegreeNodes.add(m);//insert m into S
}
}
//reassign to iterator
iterator = zeroIndegreeNodes.iterator();
}
//judge does graph has edges
for (int i = 0; i < adjacency.length; i++) {
if (adjacency[i].size() != 0){
System.out.println("AOVNetwork has cycles");
return null;
}
}
return sortedNodes;
}
Kahn’s algorithm的示意图
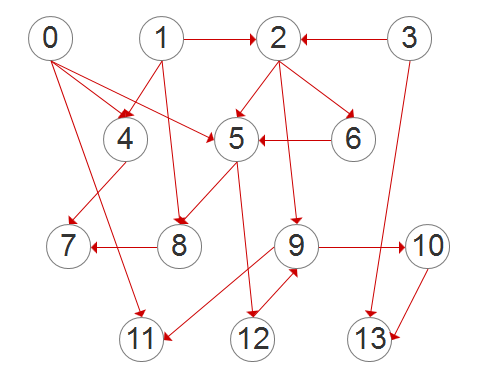
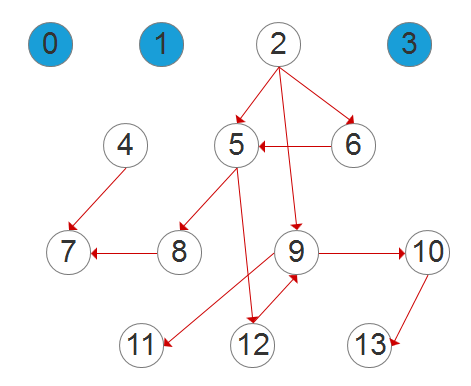
Conclusion: Kahn’s algorithm的实现十分简单明了, 仅需维护一个S集(Set of all nodes with no incoming edge)即可
references
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/topological-sorting/
- https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~ds/ppt/ch6/sld080.htm
- http://blog.csdn.net/dm_vincent/article/details/7714519
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Topological_sorting
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamiltonian_path
- http://blog.csdn.net/jnu_simba/article/details/8872847
- http://www.nhu.edu.tw/~chun/DS(I)-Ch06-Graphs.pdf
